Laparoscopy
Laproscopy is a way of performing key hole surgery. Instead of making a large incision (or cut) for certain operations, surgeons makes tiny incision and insert thin instruments with a camera attached to a telescope into an area, such as into the abdomen, to view internal organs and repair or remove tissue. For patients, laparoscopy can often mean a faster recovery from conventional surgery, less time in hospital and less trauma to the body. Conceptually,the laparoscopic approach is intended to minimise post-operative pain and speed up recovery times, while maintaining an enhanced visual field for surgeons.
Who needs Laparoscopy?
Patients with the following diagnosis will be advised laparoscopy :
1. Unexplained Infertility: Patients with longstanding infertility (more than 5 years), where semen count is normal ovarian reserves are good and endometrium lining is good but still patients is not conceiving.
2. Tubal block and hydrosalpinx: If your fallopian tubes are blocked due to presence of hydrosalpinx(Infected fluid filled in the tubes) then it is better to remove this infection by laparoscopy and proceed. This generally happens with patients who have fimbrial block, Sometimes the tubes are diseased and due to tuberculosis or PID. In such cases Laparoscopy will help. In patiemts with simple tubal block the tube can be washed and open via laparoscopy.
3. PCOD : Patients with pcod can undergo ovarian drilling via laparoscopy. This is a surgical treatment for pcod through which restoration of regular periods will happen.
4. Endometriosis: Endometriosis can be diagnosed and treated only with laparoscopy.
5. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Sometimes patients has a lot of adhesion(infected bands) outside the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes these can be diagnosed and removed through laparoscopy.
6. Fibroids: Large and small fibroids in the uterus can be removed through laparoscopy within a day,
7. Thin Endometrium: Patients with persistent thin endometrium undergo laparoscopy to evaluate any underline infection.
8. Recurrent IVF failures: Multiple IVF failure with god embryo quality should definitely undergo laparoscopy to understand the reason behind so many failure.
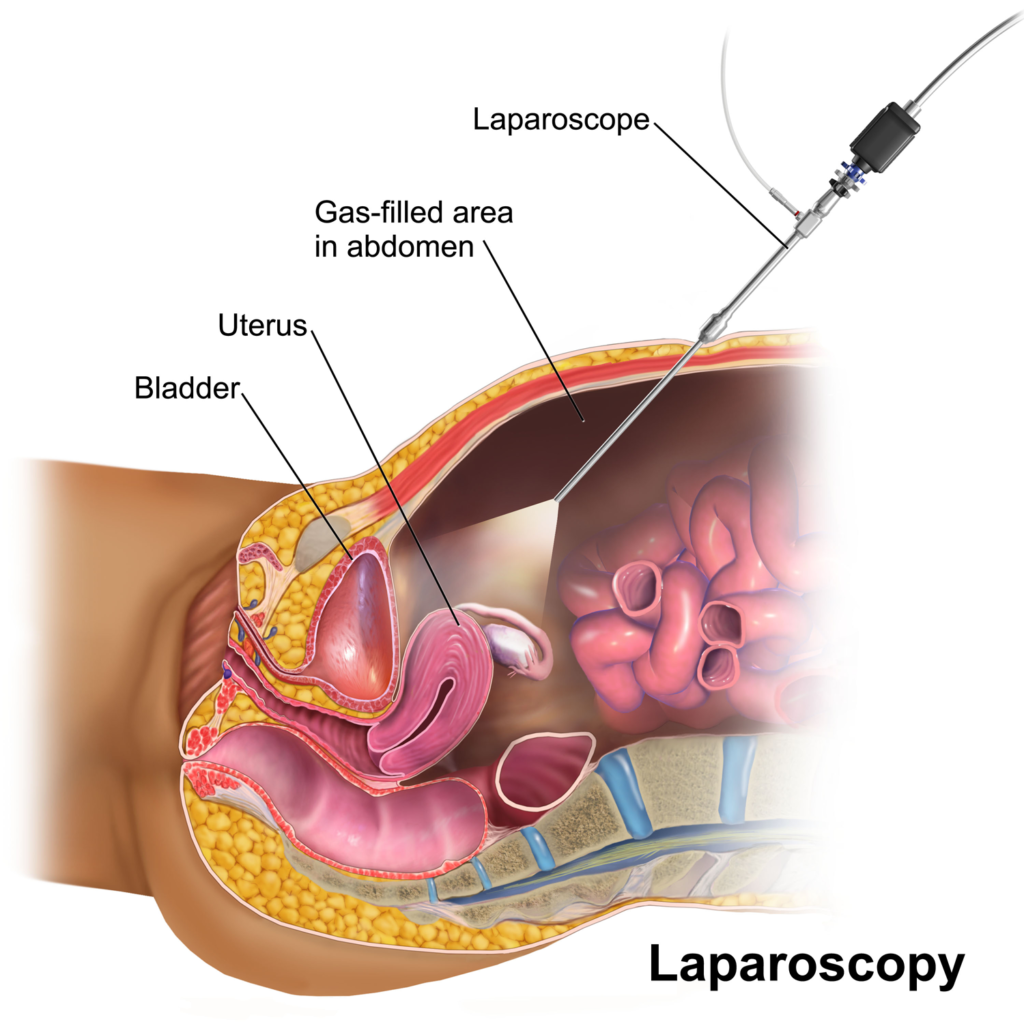
How is Laparoscopy performed ?
Laparoscopic surgery describes the performance of surgical procedures with the assistance of a video camera and several thin instruments.
During the surgical procedure, small incisions of up to half an inch are made and plastic tubes called ports are placed through these incisions. The telescope with camera attached to it is introduced through the ports which allow access to the inside of the patient.
The camera transmits an image of the organs inside the abdomen onto a television monitor. The surgeon is now able to see directly into the patient without the traditional large incision. The video camera becomes the surgeons eyes in laproscopic surgery, since the surgeon uses the image from the video camera positioned inside the patients body to perform the procedure.
As shown on the left a small laproscope is gone in the abdominal cavity and is viewing and is viewing the uterus, the ovaries and the fallopian tubes.
Advantages of Laparoscopy
- There may be less internal scarring when the procedures are performed in a minimally invasive fashion compared to standard open surgery.
- Shorter hospital stays.
- Surgeries related to womens womb (Uterus) can be performed by Laproscopy.
- Much smaller scars.
- Earlier return to full activities.
Surgeries done by Laparoscopy
- Removal of uterus.
- Removal of tumor from uterus
- Removal of tumor from ovary.
- Ectopic pregnancy surgery.
- Family planning surgery.
- Tubal surgery for blocked fallopian tubes.


