In this page we will discuss the factor in the female body that affect fertility. The good news is all these factors can be treated. Written bellow are short descriptions of all the female infertility problems.
Endometriosis

Normally the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) sheds out through the cervix every month. We call this phenomenon – menstruation. Sometimes the endometrial cells, instead of coming out from the cervix go in the pelvis through the fallopian tubes or in the myometrium through the blood vessels.
Here the endometrial cells get lodged and start growing like the endometrium in response to ovarian hormones. Growth of endometrium is completely dependent on estrogen and progesterone (ovarian hormones).
This ectopic endometrium also sheds and bleeds with every menstrual cycle, causing severe pain during menstruation.
With repeated menstruation adhesions are formed. Blood filled cysts in the ovary are called chocolate cysts. Adhesions behind the uterus cause pain during intercourse.
When endometrium gets lodged in uterine muscles, uterus gets enlarged, this condition is called adenomyosis. Women with adenomyosis complaint of heavy bleeding and severe pain during menses.
Due to adhesions, women with endometriosis have a distorted tubo-ovarian relation and often fail to conceive. The disease becomes silent when ovarian hormones are suppressed. (Pregnancy or medicines) depending on the extent of endometriosis in the pelvis, the disease is staged from 1 to 4.
In the earlier stages laparoscopic adhesiolysis and burning of endometriosis deposits, allows conception in 40% patients. In advanced stages of the disease IVF is preferable (with ovarian endometrial blood filled cysts). Ovarian follicles are destroyed hence number of eggs in a women decreases with repeated surgical removal of endometrium as there is a risk of ovarian failure, hence should be avoided. IVF is the best way to conceive with advanced endometriosis.
Hyperprolactinemia
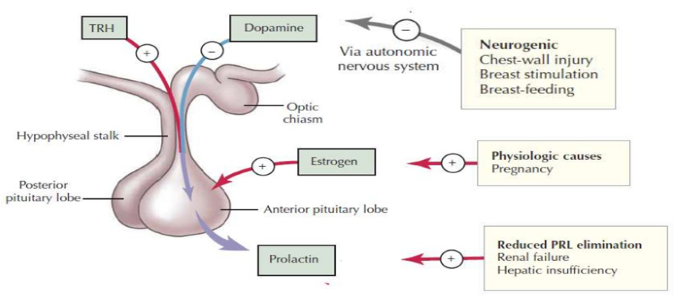
Prolactin is a hormone secreted from the PITUITARY gland to produce breast milk. When Prolactin levels are high, Pitutrary does not secrete FSH + LH hence ovulation does not occur. This happens normally during Lactation. In some women a small pituitary tumour secretes excessive Prolactin resulting in breast milk secretion, scanty menses or no menses and infertility. CABERGOLINE is drug of choice to treat these small adenomas. If the tumour is large (rarely) surgery is required.
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
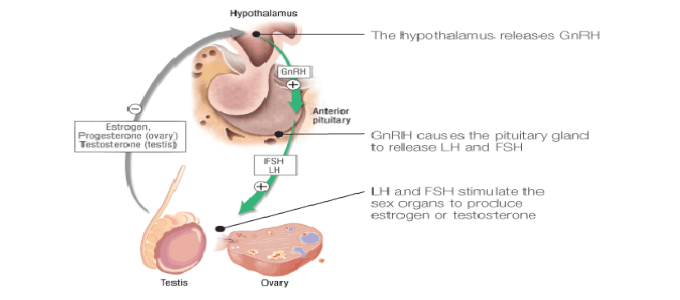
This is a condition where pituitary fails to secrete gonodotropic hormones called FSH & LH.
Normally the ovarian follicle which consist of oocyte (eggs) granulose and theca cell, start producing estrogen (female sex hormone) in response to FSH & LH from pituitary.
As the ovarian follicle grows, blood levels of estrogens rises, this estrogen supplies release of FSH and at a higher level causes LH surge and the follicle rupture, oocyte is released and what remains behind is crumpled granulosa and theca cells form the corpus luteum.
Corpus luteum produces progesterone and its life is for 14 days. So 14 days often ovulation corpus luteum dies – progesterone levels fall – the inner lining of the uterus which was supported by progesterone sheds out as menstruation.
So, for ovulation and menstruation to occur – pituitary FSH &LH are essential.
When pituitary cannot produce FSH&LH – the condition is called Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism (HH).
In this condition, women fail to get regular menses. Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism (HH) if mild, scanty menses occur at irregular intervals. Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism (HH) if severe, women will have no menses at all.
Diagnosis is done by measuring serum FSH & LH levels which are usually less than 1 MIU/ML. Treatment of this condition is very rewarding. In women desiring fertility, ovulation is induced by injection of FSH & LH.
Ovulation is monitored by Transvaginal ultra sound. Pregnancy rates are very high in these patients.
Polycystic Ovarian Disease [PCOD]

1. Do you have irregular menstrual cycles ? A. Yes B. No
2. Are you obese with hair on upper lip and chin abdomen calf muscles. A. Yes B. No
3. Has your Gynecologist has informed you that you have PCOD. A. Yes B. No
POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN DISEASE (PCOD) is a condition where a women is usually (not always) obese with irregular menses and male like hair distribution on the body (upper lip, chin, abdomen, calf muscles, inner thighs). On sonography the ovary has many peripheral follicles and ovarian volume is increased. There are two hormones coming from the Pituitary gland (based at the base of the brain) FSH and LH, normally they are in 1: 1 proportion, In PCOD, LH is three times higher than FSH. Due to which a lot of follicles starts growing in the ovary,
In the ovary there are two types of cells surrounding the egg-
1) Theca cells outside
2) Granulosa cells inside around the oocyte
LH hormone acts on the Theca cells which produce male hormone TESTOSTERONE.
Normally testosterone is converted to ESTROGEN because of FSH acting on granulose cells.
In PCOD because LH is high Theca cells are more Testosterone produce by these cells cannot be converted to estrogen. This high circulating Testosterone produces obesity, male like features and failure of ovulation.
There is a genetic link between PCOD and Insulin resistance and many PCOD women have altered GTT (glucose tolerance test) and high circulating Insulin.
How Do We Manage Pcod ?
PCOD is an inherited disorder and one has to live with it. The best treatment for any complaints of PCOD (Hirsutism, Obesity, Infertility.) is lifestyle management, like:
1) DIET which contain low carbohydrates , low fats and high proteins and fiber
2) EXERCISE this should be a resistance exercise like Weights, climbing.
Weight reduction is the first key to solve problems.
For Hirsutism (male like hair distribution) ANTI-ANDROGENS are prescribed.
For Weight gain: diet, exercise and Insulin sensitisers are given
For Ovulation Induction and Infertility Clomifene Citrate is the first drug tried. If this fails then Laproscopy and Hysteroscopy is done and Ovarian-drilling is done to remove excess Androgens from the Ovary.
40 % Patients will Spontaneously Ovulate.
1) If PCOD Drilling fails Ovulation can be induced with Gonadotrophins + IUI. This is injections of Hormones FSH and LH. There is a risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome when HCG Hormone is given for ovulation after growing folliclas with Hormones. ( FSH & LH )
In Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome the blood vessels in the peritoneum or pleura starts leaking water from the blood. Abdomen gets distended, ovaries are enlarged there is fluid collection in the abdominal cavity ( Ascitis ). Sometimes excess of fluid can make respiration difficult. In this situation fluid has to be tapped (removed with a needle) If the fluid collects in pleura (a space around lungs) repeated tapping is required. Ovarian Hyperstimulation is self limiting condition, starts on day 5 after injection HCG and disappears in 7 days. If you conceive in this state, Hyperstimulation continues for 2 weeks.
2) If you fail to conceive with Gonadotrophins + IUI for 3 cycles the next line of treatement is IVF/ ICSI.
Pregnancy rates in PCOS patients undergoing IVF / ICSI are as high as 50 % hence it is worth taking a chance with IVF / ICSI. Chances of getting more eggs and Ovarian Hyperstimulation are high along with Twin Gestations. Embryo freezing for next cycles is highly recommended.
In the ovary there are two types of cells surrounding the egg-
1) Theca cells outside
2) Granulosa cells inside around the oocyte
LH hormone acts on the Theca cells which produce male hormone TESTOSTERONE.
Normally testosterone is converted to ESTROGEN because of FSH acting on granulose cells.
In PCOD because LH is high Theca cells are more Testosterone produce by these cells cannot be converted to estrogen. This high circulating Testosterone produces obesity, male like features and failure of ovulation.
There is a genetic link between PCOD and Insulin resistance and many PCOD women have altered GTT (glucose tolerance test) and high circulating Insulin.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome [PCOS]
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age.
Infertility is one of the most common PCOS symptoms. Because the symptoms of PCOS are seemingly unrelated to one another, the condition is often overlooked and undiagnosed.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a problem in which a womens hormones are out of balance. It can cause problems with your periods and make it difficult to get pregnant. PCOS also may cause unwanted changes in the way you look. If it isnt treated, over time it can lead to serious health problems like diabetes, hypertension also called metabolic syndrome.
PCOS Symptoms
PCOS is a syndrome disease defined by a collection of signs and symptoms. The symptoms of PCOS that one patient experiences can be very different from the symptoms of another patient. If you have two or more of the following symptoms, you need to have a thorough checkup to determine if you need PCOS treatment:
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Infertility
- Male like hair distribution on the body(hirsutism)
- Thinning hair on the scalp
- Weight gain
- Skin problems, including skin tags, darkening skin and acne
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound.
Complications of PCOS
The common PCOS symptoms are difficult enough for most women, but some will experience further complications, including:
- Diabetes, elevated insulin levels or insulin resistance
- Heart and blood vessel problems
- Uterine cancer
- Sleep apnea
Each of these problems can be life threatening, which is why treatment for PCOS is so important.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease [PID]

The female reproductive track consists of a vagina, cervix, uterus, two fallopian tubes and ovaries. Of these the fallopian tubes are most delicate and can get infected leading to their damage and infertility.
Normally infections to reproductive tract are sexually transmitted and lead to damage and infertility.
Nature protects our reproductive tract in many was –
- The vagina has a very acidic pH,
- The cervix has a thick plug which disallows bacteria to enter the reproductive tract.
- The uterine lining sheds at every menstrual cycle and does not allow infection to persist inside the uterus.
There are some infections which can reach the fallopian tubes in spite of all this protection. These are bacteria called.
- Chlamydia
- Mycloplasma
- Gonococci
Chlamydia are the commonest sexually transmitted organisms. The male reproductive tract harbous these organisms and are transmitted to the female.
In the female, they remain symptom less till they reach the fallopian tubes when she experiences pelvic pain. Bacterial infections change the inner lining of the fallopian tubes, cause scarring, obstruction,oedema and distention of tubes (Hydrosalpinx).
Pregnancy can rarely occur in such damaged tubes. Pelvic infections should be rigorously treated to prevent damage to fallopian tubes. IVF-ICSI is the treatment of choice for damaged tubes. Hydrosalpinx should be removed by laproscopy prior to IVF. Couples having infections should be treated with antibiotics before starting IVF.
Premature Overian Failure [POF]
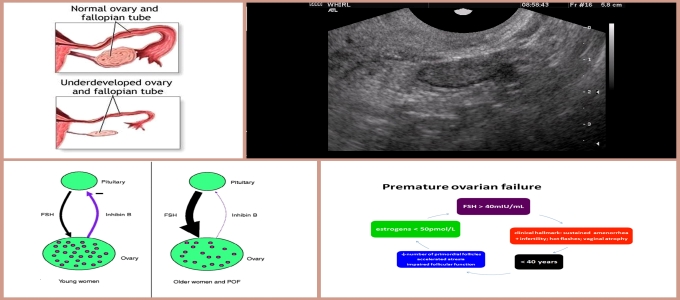
PREMATURE OVARIAN FAILURE ( Premature Menopause. ) When the number of eggs in the ovary reduces dramatically, ovaries become small, and on 2nd day of menses the number of follicles in the ovary are less than 4. If we do AMH levels (ANTI MULLERIAN HORMONE) it is low < 1. All this normally happens when a women crosses 45 yrs of age – natural onset of Menopause. In some women this process starts early and menstrual cycles become irregular, scanty, sexual drive drops, and she is infertile. All the medicines like DHEAS are tried to increase ovarian reserves but not all succeed. For women with low AMH, High FSH, and Poor Antral Follicle count – IVF should be started early to get the quickest chance of Pregnancy.
Uterine Fibroids

Fibroids are benigen tumours of the uterus made up of fibrous tissue. They arise in the Myometrium, protrude in the uterine cavity or outside the uterus. Their size varies from 1 to 30 cm or even more.
When fibroids are present in the myometrium pelvic pain, heavy uterine bleeding, dysmenorrhea and infertility are the chief symptoms. It is better to remove fibroids surgically ( Myomectomy ) before starting fertility treatment. When fibroids are less than 5 cm and less than 3 in number can be removed by LAPROSCOPY. (LAP-MYOMECTOMY) women with fibroids and infertility have a good chance of conception after Myomectomy. Sometimes these myomas regrow and may need repeated surgery
Polyps

Polyps: They are small cellular structures that grow in the inner wall of the uterus. Over growth of cells in the endometrium leads to uterine polyps. Small polyps don’t interfere in the reproductive process; whereas large polyps need to be removed. Large polyps increase the risk of miscarriage. They are oval or round in shape and they remained attached to the endometrial wall. Symptoms of uterine polyps include heavy bleeding, spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods, infertility and vaginal bleeding after menopause. Small polyps might regress at any stage. There is no non invasive treatment for polyps
IU Adhensions/Ashermans Syndrome
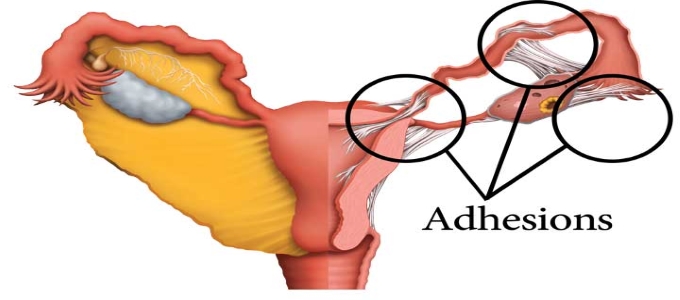
Intrauterine adhesions, or intrauterine synechiae, are a condition in which scar tissue develops within the uterine cavity. Intrauterine adhesions accompanied by symptoms (e.g. infertility, amenorrhea) are also referred to as Asherman syndrome. The degree of adhesion formation and the impact of the adhesions on the contour of uterine cavity vary greatly. With minimal disease, thin bands of tissue stretch between surfaces of the uterine cavity, whereas severe disease is characterized by complete obliteration of the cavity, with the anterior wall of the uterus densely adherent to the posterior wall. These may impede menstrual flow or interfere with conception or pregnancy.
Ovirian Cyst

The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They’re located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that produce eggs, as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Most women will experience a cyst on the ovaries at least once, and most are painless, cause no symptoms, and are discovered during a routine pelvic exam. Symptoms of an ovarian cyst include nausea, vomiting, bloating, painful bowel movements, and pain during sex. In rare cases, an ovarian cyst can cause serious problems, so it’s best to have it checked by your doctor. There are various types of ovarian cysts, such as dermoid cysts and endometrioma cysts. However, functional cysts are the most common type. The two types of functional cysts include follicle and corpus luteum cysts.
Tubal Blocks

Approximately 20% of female infertility can be attributed to tubal causes.[1] Distal tubal occlusion (affecting the end towards the ovary) is typically associated with hydrosalpinxformation and often caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.[1] Pelvic adhesions may be associated with such an infection. In less severe forms, the fimbriae may be aggluntinated and damaged, but some patency may still be preserved. Midsegment tubal obstruction can be due to tubal ligation procedures as that part of the tube is a common target of sterilization interventions. Proximal tubal occlusion can occur after infection such as a septic abortion. Also, some tubal sterilization procedures such as the Essure procedure target the part of the tube that is near the uterus.


